
How to validate your marketplace idea
Learn – Dittofi Marketplace Archives How to validate your marketplace idea “No one knows for sure if a startup idea will work.” Jared Friedman, Y
App development happens in ordered phases.
These phases are shown in the graph below.
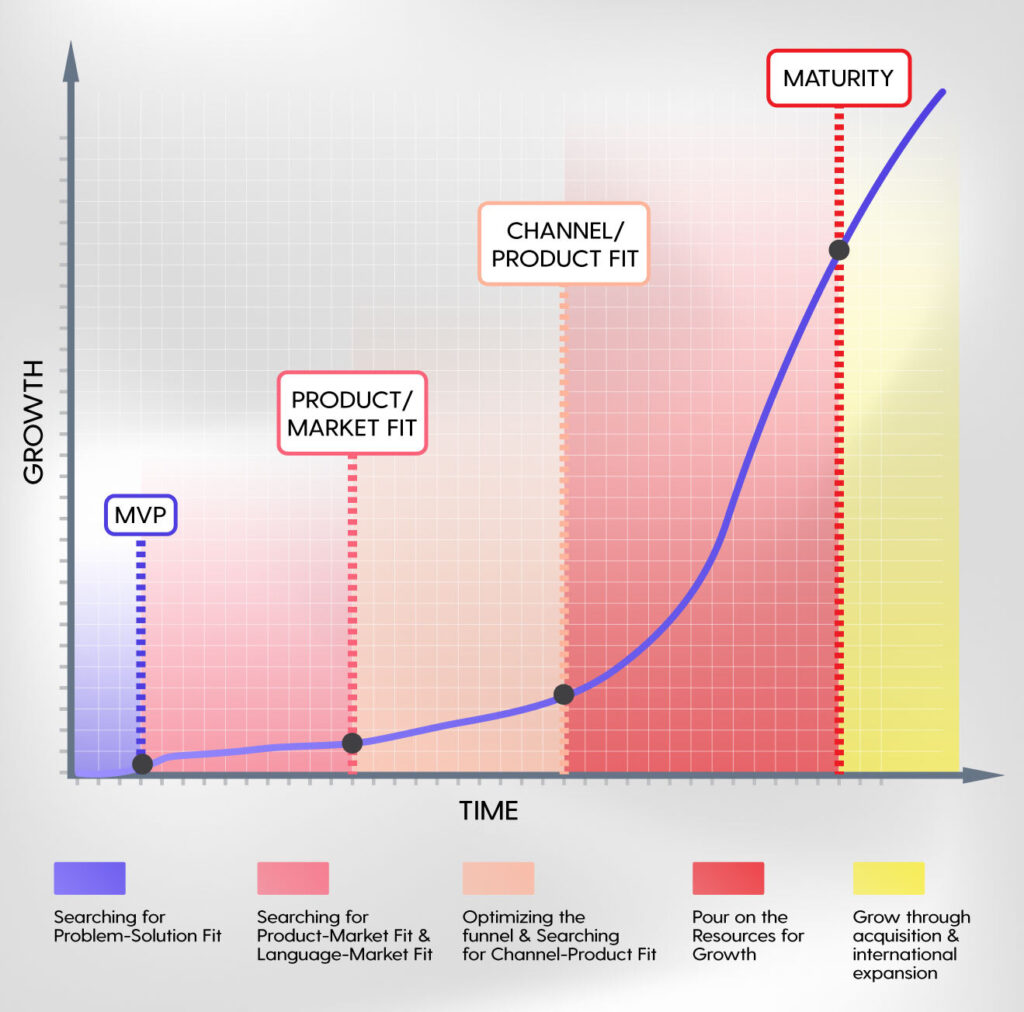
At Dittofi, we have created the worlds first hybrid no-code platform that can be used to build & scale apps 10x faster & without writing any code. We have also created a set of tools to help companies navigate each phase of their app development. This is because we saw that many companies need guidance on how to adopt such a powerful software within a business context.
Dittofi’s Idea Validation Board is one such tool that you can use to help validate idea stage initiatives.
*Please note The Idea Validation Board is a concept that has been is adapted from Trevor Owens Lean Startup Validation Board, 2012.
We will cover:
The Idea Validation Board is a tool for structuring how to think through the development of a new business initiative. It is appropriate for anyone developing a new tech product or business initiative i.e. startups, SMEs & enterprises. The tool is structured around concepts taken from the lean startup approach to app development.
You can download your own copy of the Idea Validation Board & try filling in each section by yourself or with your team.
The Idea Validation board is broken down into four parts: pivot tracker, build (experiment), measure & learn (validated learning).
At the top of the board, you have an area where you will track your apps pivots over time.
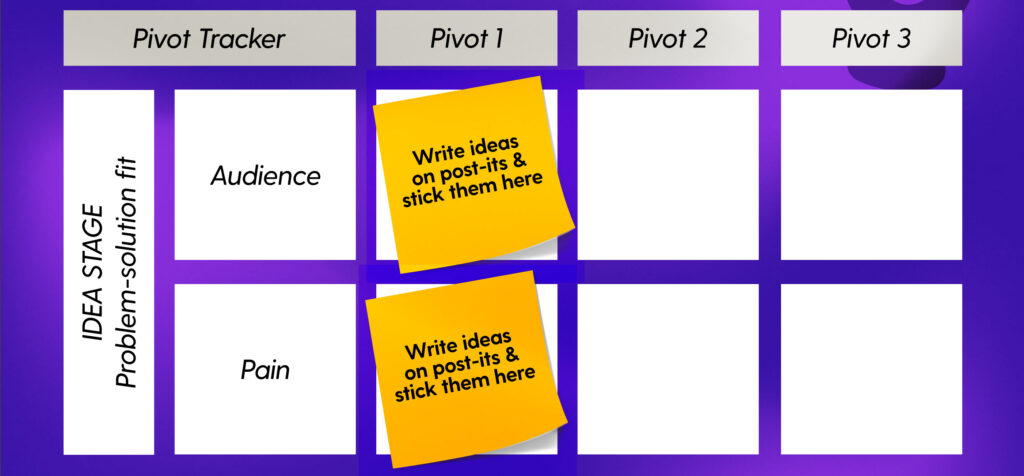
At the idea stage, each pivot is built out of two core assumptions:
A new pivot occurs whenever one of our core assumptions about the customer or the problem is proved invalid.
Every successful startup has gone through multiple pivots. For instance, YouTube started it’s life as a video dating site, Netflix began as a mail order service for DVDs & Slack started out as a computer game called Glitch.
Since it takes time & money to test your assumptions & then to pivot, the startups objective is to minimize the time & money spent on each pivot. Therefore, in the Lean Startup methodology, a startup’s runway (how long the business has before it runs out of money), is re-defined as the number of pivots it can still make.
In the middle of Dittofi’s Idea Validation Board is a space to build an experiment.
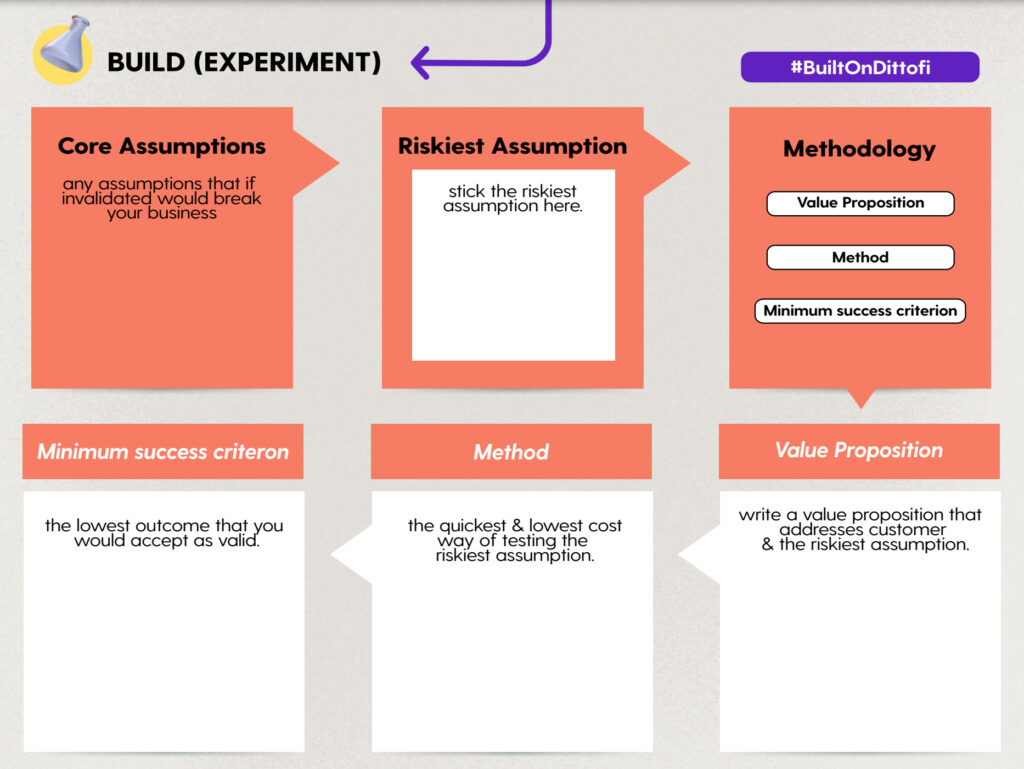
The Lean Startup methodology re-defines a “product” as an experiment. This is because we are going to build a “product” that will be used to run experiments. “Product” in this context does not mean a full blown software application. It might mean that you just need to go & build a list of questions to ask prospective customers about their pain. It could also mean landing pages or mini applications that can be used to learn more about your customers & validate or invalidate core assumptions about our target audience & their pain.
Write out the core assumptions that you are making about your customer & their pain. Next, choose the riskiest assumptions from your list of core assumptions & devise a methodology to test the riskiest assumption.
At the idea stage, you do not need to build a full blown product to run an experiment. You simply need to:
Your value proposition should clearly articulate the assumption about the audience, their problem, your solution to that problem & the benefits of your solution. The easiest way to do this is to setup a simple landing page that clearly communicates the value proposition.
Various methods exist to test your riskiest assumption. For example, you could use (1) customer interviews, (2) pitch your product to prospective buyers for some form of exchange e.g. money, an email addresses, time & anything else that your customer is willing to give to you or even (3) deliver the service to your customers.
At this stage, you are going to be exclusively focused on easy to track, customer focused metrics. These include, the number of customers willing to leave an email address, customer discussions, customer feedback, conversion rates, per customer revenue etc.. Data collection methods can include face to face discussions, using Google Analytics to track website traffic, counting up the number of people who leave an email address & so on.
It’s important to remember that each experiment is a potential pivot. As such, our objective is to keep the cost of each experiment as low as possible. At Dittofi, we use hybrid no-code (visual programing, AI & auto code generation technology) to minimize the time & cost associated with building each new experiment.
After designing the experiment, the next thing to do is to run your experiment. For this stage you need a go-to-market (GTM) strategy.
There are various ways to put your product in front of customers. For example, you could (1) ask people you know who you think have the problem, (2) post on social media channels, (3) buy a database of emails & do cold email outreach, (4) run targeted ads & so on.
It’s important to choose a strategy which is low cost but is also time effective. Running a Google Ad campaign is quick & easy to setup & can put your app in-front of users who are actively searching for the solution provided by your value proposition. This may be easier to organize than messaging 1000 people on Linkedin.
Your go-to-market will allow you to collect data on each of your users & to understand if your product is going to be successful or not. During this stage you should aim to speak with as many potential users of your product as possible. This is because speaking with customers is the best way to understand what their pain is. There are a number of ways that you can utilize technology to help speed up data collect & better understand your customer.

In the bottom right is a space to record the core assumptions that you’ve validated with data.

In the lean method, we re-define progress as validated learning.
Validated learning is the number of valuable truths that the startup has discovered about their core assumptions. For example, does the assumption that you’re testing meet the minimum success criteria. If not, the assumption has been invalidated & you need to go back to the core hypothesis & pivot. If your assumption has been validated, then you can test your next riskiest assumption.
Once you’ve found a set of core assumptions that works, it’s time to build your minimum viable product (or MVP), which will go through the same “build, measure, learn” feedback loop.
If you’re already at this stage, check out Dittofi’s MVP Lean Validation Board.
Pivoting is an essential part of any innovative new business initiative. This is because innovation by definition means that you are exploring the market for something completely new. Exploration takes time & will cost some money. However, if you’re able to keep the cost of each pivot low then you will maximize your chances of finding a core set of assumptions that actually make sense. Once this has happened you’ll be ready to build your minimum viable product.
At Dittofi, we use a combination of visual programing, AI & auto code generation technology so that you can keep the cost of running each pivot super low. You can use Dittofi to build landing pages, hooks to collect email addresses, test new value propositions, build more advanced tests, track the results of each experiment &, when you’re ready, convert your product tests into an MVP that can eventually scale into a growth stage app. Dittofi lets you do this all without the costs associated with traditional product development.
In the next article, let’s take a practical look to validate an idea for a two-sided marketplace.

How to validate your marketplace idea
Learn – Dittofi Marketplace Archives How to validate your marketplace idea “No one knows for sure if a startup idea will work.” Jared Friedman, Y

How to build an app without coding
How to build an app without coding By James Virgo You do not need to know how to code in order to build an app

Which no-code platforms export code in 2025?
Which no-code platforms export code in 2023? By James Virgo No-code is great for rapid app development, but no-code has been proven to be shockingly

⸺ Receive the latest news
Get notified about new articles and events